The Firewall.cx Wireless LAN Key Generator will allow the generation of a WEP or WPA ASCII based encryption key and will provide the equivalent HEX or ASCII string so it can be inserted directly into a Cisco Access Point configuration.
As many engineers know, it is a common problem that when configuring a WEP encryption key in a Cisco Access Point, the IOS will not allow the input of the actual ASCII key, but instead requires the HEX equivalent. With our WLAN Key generator, simply insert your desired pass phrase and it will generate the necessary HEX value encryption key that needs to be used in the CLI or Web-Based configuration of the Cisco Access Point.
The Wireless LAN Key Generator allows for quick and valid WEP/WPA key generation.
You can use the Random WEP/WPA Key Generator to generate a random WEP or WPA key. Simply choose the desired key length using the drop-down menu, and one will be generated for you.
The WEP/WPA Key Generator supports 64bit, 128bit, 152bit & 256bit WEP keys, and 160bit, 504bit WPA/WPA2 keys for maximum security.
Alternatively, if you require to generate a key based on a custom passphrase (most cases), you can use the Custom WEP/WPA Key Generator. Just enter your password phrase into the Custom WEP/WPA Key Generator - ASCII text fields, and its HEX equivalent will be generated automatically. You can also insert the HEX Value and the system will reveal the actual ASCII value - handy if you want to discover what password phrase has been used for the encryption.
WEP/WPA Key Generator
Random WEP/WPA Key Generator
Key Length:
ASCII :
HEX :
Custom WEP/WPA Key Generator
Note: use 5/13/16/29 characters for 64/128/152/256-bit WEP Encryption
ASCII : #
HEX :
Calculate Key Now! Clear Form
Notes: WEP encryption uses 24 bit "Initilization Vector" in addition to the "secret key". Therefore, 40 bit WEP can be refered to as 64 bit WEP, and 104 bit can be refered to as 128 bit, depending on whether the "initialization vector" is counted or not.
All About Wireless
Everything is Wireless
Sabtu, 03 Desember 2011
Wireless Communication
Wireless communication uses radio frequencies (RF) or infrared (IR) waves to transmit data between devices on a LAN. For wireless LANs, a key component is the wireless hub, or access point, used for signal distribution (see Figure 8-8).
Figure 8-8 Wireless Network
To receive the signals from the access point, a PC or laptop must install a wireless adapter card (wireless NIC). Wireless signals are electromagnetic waves that can travel through the vacuum of outer space and through a medium such as air. Therefore, no physical medium is necessary for wireless signals, making them a very versatile way to build a network. Wireless signals use portions of the RF spectrum to transmit voice, video, and data. Wireless frequencies range from 3 kilohertz (kHz) to 300 gigahertz (GHz). The data-transmission rates range from 9 kilobits per second (kbps) to as high as 54 Mbps.
The primary difference between electromagnetic waves is their frequency. Low-frequency electromagnetic waves have a long wavelength (the distance from one peak to the next on the sine wave), while high-frequency electromagnetic waves have a short wavelength.
Some common applications of wireless data communication include the following:
Accessing the Internet using a cellular phone
Establishing a home or business Internet connection over satellite
Beaming data between two hand-held computing devices
Using a wireless keyboard and mouse for the PC
Another common application of wireless data communication is the wireless LAN (WLAN), which is built in accordance with Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 standards. WLANs typically use radio waves (for example, 902 megahertz [MHz]), microwaves (for example, 2.4 GHz), and IR waves (for example, 820 nanometers [nm]) for communication. Wireless technologies are a crucial part of the today's networking. See Chapter 28, "Wireless LANs," for a more detailed discuss on wireless networking.
Source : http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=31276&seqNum=3
Figure 8-8 Wireless Network
To receive the signals from the access point, a PC or laptop must install a wireless adapter card (wireless NIC). Wireless signals are electromagnetic waves that can travel through the vacuum of outer space and through a medium such as air. Therefore, no physical medium is necessary for wireless signals, making them a very versatile way to build a network. Wireless signals use portions of the RF spectrum to transmit voice, video, and data. Wireless frequencies range from 3 kilohertz (kHz) to 300 gigahertz (GHz). The data-transmission rates range from 9 kilobits per second (kbps) to as high as 54 Mbps.
The primary difference between electromagnetic waves is their frequency. Low-frequency electromagnetic waves have a long wavelength (the distance from one peak to the next on the sine wave), while high-frequency electromagnetic waves have a short wavelength.
Some common applications of wireless data communication include the following:
Accessing the Internet using a cellular phone
Establishing a home or business Internet connection over satellite
Beaming data between two hand-held computing devices
Using a wireless keyboard and mouse for the PC
Another common application of wireless data communication is the wireless LAN (WLAN), which is built in accordance with Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 standards. WLANs typically use radio waves (for example, 902 megahertz [MHz]), microwaves (for example, 2.4 GHz), and IR waves (for example, 820 nanometers [nm]) for communication. Wireless technologies are a crucial part of the today's networking. See Chapter 28, "Wireless LANs," for a more detailed discuss on wireless networking.
Source : http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=31276&seqNum=3
Jumat, 02 Desember 2011
Wireless Transmitting Devices
Microwaves:Microwaves are point to point towers or satalites call geocentric satelites, point to point means the towers or satelites must be in direct view of each other and for towers they must be less then 30 km apart for the signal to reach the other tower, but if a tower is transmitting to a satelite once the microwave goes through the atmosphere wich is only 16 km away the signal can travel for ever. microwaves can not travel through and objects including rain, this is the reason u often lose reception in storms. microwaves often are used for mobile phones but like other transmitting devices can be used for transmitting data.
Radio: Radio waves are generally used for mobile phones, wireless local are network (LAN), bluetooth and many more, radio waves are an alternative current (ac) wich is applied to the antena, when excited by this alternating current, the antena then radioates radio-radio waves in addition to there use in broadcasting, transmitters are a necessary component parts of many electronic devices, that communicate by radio.
Infrared: Infrared transmitting devices are things like, remotes for the tv, coredless modems, fire sensors, motion detectors, etc. you cannot see infraredwaves but u can feel it, when u put your hand nere a fire and feel the warmpth, that is a version of infrared transmittion, infrared cannot not get thought object for example if you put your hand infront of the remote it won't work, but it can reflect off of things such as mirrors and glass.
Radio: Radio waves are generally used for mobile phones, wireless local are network (LAN), bluetooth and many more, radio waves are an alternative current (ac) wich is applied to the antena, when excited by this alternating current, the antena then radioates radio-radio waves in addition to there use in broadcasting, transmitters are a necessary component parts of many electronic devices, that communicate by radio.
Infrared: Infrared transmitting devices are things like, remotes for the tv, coredless modems, fire sensors, motion detectors, etc. you cannot see infraredwaves but u can feel it, when u put your hand nere a fire and feel the warmpth, that is a version of infrared transmittion, infrared cannot not get thought object for example if you put your hand infront of the remote it won't work, but it can reflect off of things such as mirrors and glass.
Rabu, 30 November 2011
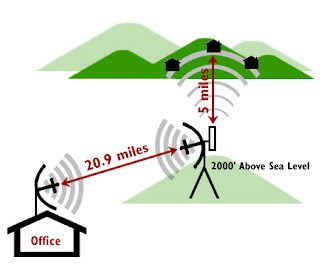
Covad Wireless
About Covad Wireless ..
Fast install, high performance and competitive pricing on business class Internet access.
Covad Wireless, formerly known as NextWeb, Inc., operates one of the nation’s
largest fixed broadband wireless networks focused on serving business customers.
Its solutions range from T1 replacement to high-capacity service with data speeds of
up to 45Mbps. Covad Wireless serves over 4,000 small and medium-sized businesses in the San Francisco Bay Area, Greater Los Angeles
area, Chicago and Las Vegas.
Covad Wireless is a division of Covad Communications.
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)